The AI index unveiled: how artificial intelligence is reshaping jobs and skills
Key Insights from the Anthropic AI Index on Job Disruption, Emerging Opportunities, and the Future of Work
AI is transforming industries at breakneck speed—but what does that mean for jobs? This article unpacks the evolving relationship between AI and employment, using insights from the Anthropic AI Index to explore job displacement, shifting skill demands, and the realities behind common fears such as automation and workplace monitoring. Beyond the concerns, we reveal how AI can enhance human work, create new opportunities, and redefine the future of business. Dive in to discover what AI’s rapid rise means for companies and employees—and how to stay ahead in this new era.
What You Will Learn in This Article:
How AI is reshaping industries, from job displacement risks to emerging opportunities
The evolving demand for skills and why mid-to-high wage jobs are most affected
Key insights from the AI Index on AI adoption, augmentation, and automation trends
The broader implications of AI on work, wages, and human-AI collaboration
The Uncertain Impact of AI on the Workforce
As Artificial Intelligence transforms industries at an unprecedented pace, its effects on the workforce are complex and uncertain. While some fear widespread job losses, others see new opportunities emerging. The latest insights from the AI Index reveal that this landscape is marked by both emerging trends and significant uncertainties, making long-term predictions challenging.
Concerns Surrounding AI in the Workplace
A primary concern is the potential for AI to replace numerous jobs, especially in knowledge-based and administrative roles. Many office-based positions face greater risk, whereas jobs requiring manual skills—such as plumbing and construction—are less likely to be automated. Additional concerns include:
Shifting skill demands – as AI takes over routine cognitive tasks, workers may need to develop new skills, particularly in data analysis, AI oversight, and human-centred problem-solving. This transition could leave many employees struggling to adapt
Job polarisation – AI could widen the gap between high-skilled, high-paying roles and lower-skilled jobs, reducing opportunities for middle-income workers
Workplace monitoring and productivity pressures – AI-driven performance tracking tools may increase workplace surveillance, raising ethical concerns and putting additional pressure on employees
Loss of entry-level jobs – many junior roles involve repetitive tasks that AI can automate, potentially making it harder for people to gain initial work experience
Economic disruption – rapid AI adoption could lead to short-term job displacement before new roles emerge, creating instability in certain industries
While these concerns are valid, AI’s full impact remains uncertain, and much will depend on how businesses, policymakers, and workers adapt to these changes.
Understanding the AI Index
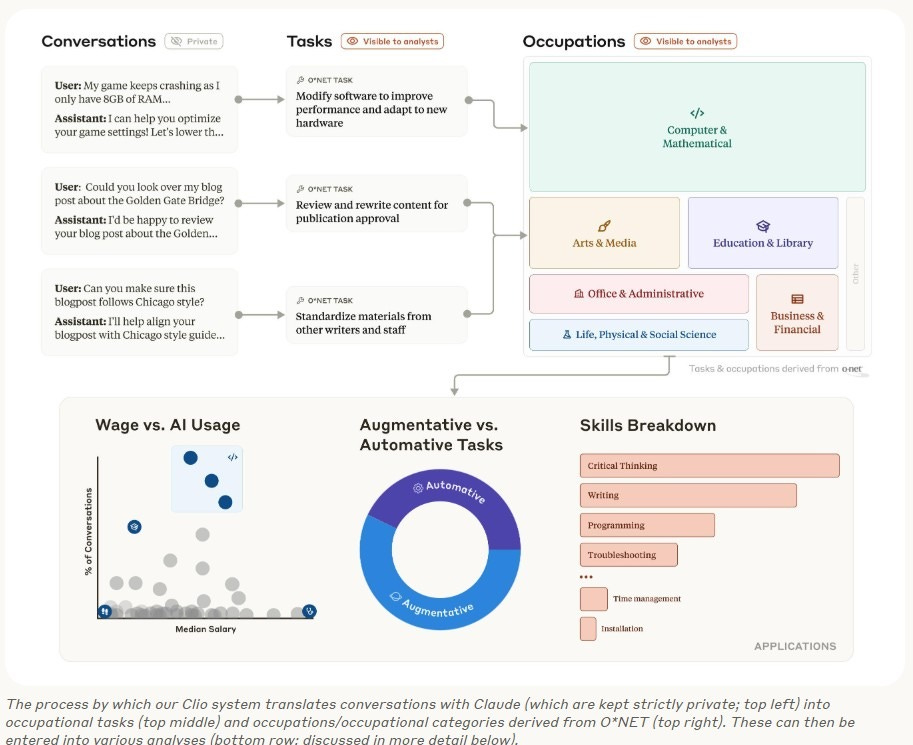
The AI Index aims to track and understand how Artificial Intelligence is shaping labour markets and the broader economy over time. To do this, it moves beyond broad discussions of job losses or gains and instead takes a more detailed approach to analysing how AI interacts with different types of work. Rather than focusing on entire occupations, the index examines specific job tasks—some of which are more susceptible to automation than others. This approach provides a more nuanced perspective on AI’s real impact, moving beyond the often-simplistic debate of whether jobs will disappear entirely.
To build this analysis, researchers used segregated and anonymised datasets, breaking down roles into their core activities. By assessing the nature of these tasks—whether they involve routine cognitive work, complex decision-making, or manual dexterity—the index highlights which aspects of a job are most at risk of automation. This task-level approach allows for a more accurate projection of AI’s influence across different industries.
One of the key tools behind this effort is a Clio, developed by Anthropic. Clio leverages AI-driven conversations to map tasks to specific occupations, enabling deeper analysis of automation potential and workforce shifts. This data-driven approach helps to provide a clearer picture of AI’s evolving role in the workplace.
What the Index Is Saying
The AI Index provides a detailed view of how AI is currently being used across different industries, professions, and tasks. Rather than focusing solely on broad predictions about job loss or transformation, the index highlights specific trends that reveal where AI is making the biggest impact, how it is reshaping work, and which roles are most affected.
The findings suggest a more nuanced picture than the common narrative of AI replacing human workers. While AI adoption is increasing, it is primarily being used as a tool for efficiency and augmentation rather than full automation. However, its influence varies significantly across sectors, wage levels, and skill categories. Below are some of the key insights from the AI Index.
Predominant Use in Technical Fields
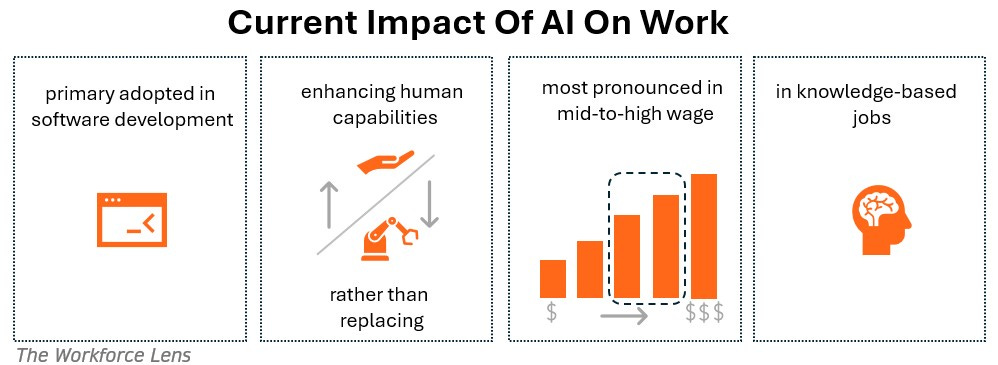
AI adoption is most prominent in technical and knowledge-based industries, particularly in software development and technical writing. According to the AI Index, 36% of occupations incorporate AI in at least 25% of their tasks, while only 4% of occupations utilise AI for over 75% of their tasks. This suggests that while AI is increasingly integrated into various workflows, full automation remains rare.
Creative industries have also seen notable AI adoption, with 10.3% of AI usage reported in arts, design, entertainment, and media. This indicates that AI is not limited to technical fields but is also being leveraged for creative work, such as content generation and digital design.
Augmentation Over Automation
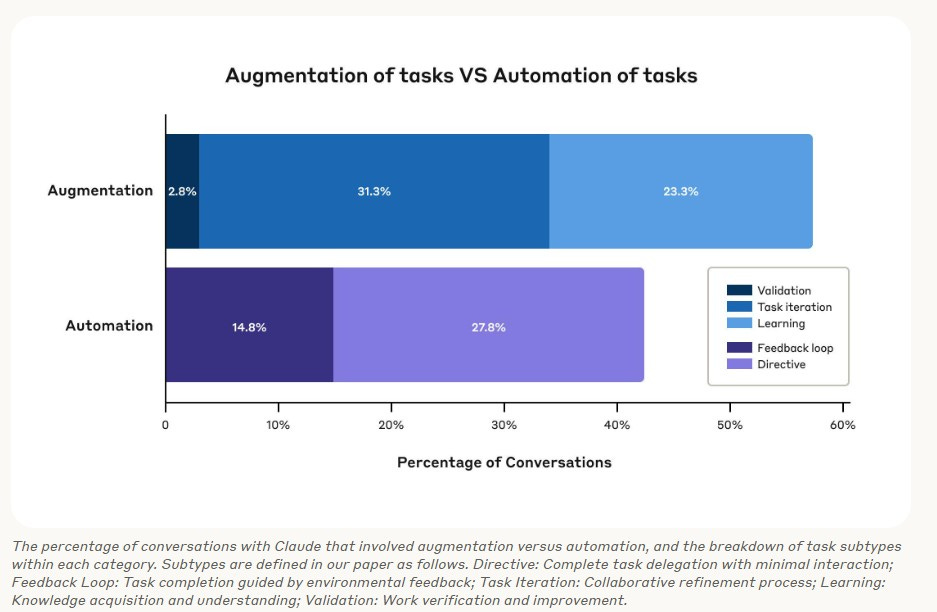
A key takeaway from the index is that AI is being used more to enhance human capabilities rather than replace them entirely. The data shows that 57% of AI applications are focused on augmentation—helping workers complete tasks more efficiently—while only 43% involve full task automation. This supports the view that AI is primarily acting as a productivity tool rather than an outright job replacement mechanism.
Sector-Specific AI Adoption
Beyond technical fields, it is essential to consider how AI is being adopted in other industries. For instance, sectors such as healthcare and manufacturing are also experiencing increased AI utilisation, particularly in areas such as diagnostics, supply chain management, and customer service. These applications suggest that AI is becoming a critical tool for efficiency and innovation across diverse job categories.
Correlation with Wage Levels
The index highlights that AI adoption is more prevalent in mid-to-high wage professions. Roles such as computer programmers and data scientists are among the most affected, where AI is used extensively to improve efficiency and automate repetitive tasks.
Interestingly, AI adoption is relatively low in both the lowest and highest-paid occupations. While low-wage roles often involve manual or service-oriented work that AI struggles to automate, high-earning professionals—such as executives, lawyers, and senior consultants—tend to rely on complex decision-making, interpersonal skills, and strategic thinking, which remain challenging for AI to replicate.
Human-AI Collaboration Trends
The data also underscores that AI is more commonly used as a collaborative tool rather than a full replacement. In 57% of cases, AI augments human work, supporting tasks such as validation, learning, and iterative improvements. However, in 43% of cases, AI is used to fully automate certain processes, indicating that while augmentation is the dominant trend, automation is still a reality for some roles.
Global Variations and Public Perception
AI usage varies significantly across regions, with some countries adopting AI technologies more rapidly than others. This discrepancy highlights the need for policies that support responsible AI integration while considering local contexts. Furthermore, public perception of AI's impact on employment is evolving. As discussions about AI's role in the workforce continue, policymakers and workers alike are increasingly focused on the implications for job security and the importance of developing skills that complement AI technologies.
In summary, the AI Index underscores a complex and dynamic relationship between Artificial Intelligence and the workforce. While concerns about job displacement persist, the data also highlights opportunities for augmentation, collaboration, and the need for evolving skill sets in a rapidly changing employment landscape. AI is primarily adopted in technical fields, especially software development, where it enhances human capabilities in 57% of applications rather than fully replacing jobs. Although AI is also used in creative industries, its impact is most pronounced in mid-to-high wage professions, particularly in knowledge work, with lower adoption in low-wage and high-level roles that require complex decision-making.
The Future of Work: Embracing AI's Transformative Role
As we enter an era dominated by Artificial Intelligence, it is vital to consider the broader implications of this technological shift. The future of work will be shaped not only by AI advancements but also by economic conditions, political frameworks, and cultural attitudes.
Economically, AI has the potential to boost productivity and transform job markets, yet it also raises concerns about job displacement and the need for new skills. Politically, different countries will adopt varying regulations that could create significant disparities in AI integration and its benefits. Culturally, societal attitudes will influence how readily AI is accepted as a partner in the workplace.
Understanding these interconnected factors will be essential as we explore how AI is reshaping office jobs, enhancing productivity, and driving innovation while maintaining the importance of human insight and ethical considerations.
Automation of Repetitive Tasks and Historical Perspectives: AI as an Extension of Human Capability
Historically, technological advancements have served as extensions of our capabilities, and AI is no different. Just as the introduction of the calculator revolutionised mathematics or word processors transformed writing, AI is set to enhance our office productivity. These innovations have consistently demonstrated that tools can significantly expedite workflows and improve accuracy. As we look ahead, it is likely that Artificial Intelligence will play a pivotal role in reshaping office jobs by automating the most repetitive tasks. Tools such as Microsoft Copilot are already offering support in handling various responsibilities, although not always perfectly. This marks just the beginning of a significant transformation. For instance, composing emails has become quicker and more efficient, while AI-enhanced Excel applications allow for streamlined data analysis and reporting, making office work not only faster but also more productive.
Physical Labour: The Continued Need for Human Skills
In occupations that involve physical labour, such as plumbing or construction, significant changes are not expected in the short term. Although robots may assist with certain functions, the need for skilled human workers will remain paramount. The hands-on nature of these jobs necessitates a level of adaptability and problem-solving that current AI technologies cannot replicate.
Complex Problem-Solving and Creativity: The Human Touch Remains
While tasks requiring deeper cognitive engagement or complex problem-solving are unlikely to experience immediate changes, AI will provide valuable assistance in these areas. The human brain remains irreplaceable—at least for now. The unique capacity for critical thinking and emotional intelligence ensures that, despite advancements, many professional roles will continue to rely on human insight.
Similarly, the creative industry may witness an evolution due to AI's influence. Rather than replacing human creativity, AI is poised to act as a supportive tool that enhances and extends our ideas. This partnership can lead to innovative outcomes, allowing creators to explore new possibilities and push the boundaries of their work.
Education and Future Skill Requirements: Preparing for AI's Role
As AI serves as an extensive source of knowledge, it is crucial to remain vigilant about its limitations, including the potential for misinformation or "hallucinations". This reality necessitates a shift in education, promoting critical thinking and teaching students to discern credible sources while leveraging AI as a supportive tool. Furthermore, as AI continues to integrate into the workplace, skills such as adaptability, tech literacy, and emotional intelligence will become increasingly important for employees to thrive.
Ethical Considerations and Collaboration: Navigating the Challenges Ahead
As AI tools become more integrated into everyday work, it is essential to address the ethical implications of AI in the workplace, including privacy concerns, job displacement, and the need for regulations to ensure fair usage. Establishing guidelines that protect both employees and employers from potential misuse is crucial. Furthermore, effective collaboration between humans and AI can lead to improved outcomes across various industries. By working together, teams can enhance productivity and foster innovation, resulting in better decision-making and more efficient processes. Successful human-AI partnerships are already emerging, demonstrating the potential for synergy in navigating the challenges
Human-Centric Services: The Premium Value of Personal Interaction
Looking towards the future, human-based services are likely to attain a premium status, contrasting with standardised services provided by chatbots or robots. As automation becomes commonplace, the human touch in service industries will be valued more highly, distinguishing personal interactions from automated responses.
Reflect on Your Future
As AI continues to reshape the workforce, it is vital for individuals to consider their own skills and career trajectories. Take a moment to reflect on how your current skills align with the evolving job market. Are there areas where you could improve or expand your expertise? Engaging with online courses or training programmes can help you adapt and thrive in this new landscape. Your proactive steps today can ensure you remain relevant in the future world of work. How do you see AI impacting your role in the next few years?
Conclusion: Navigating the Rapid Evolution of Work
In an era of rapid transformation, we must consider not only technological advancements but also the shifting political landscape that influences how these changes are implemented globally. The pace of AI adoption can vary significantly between countries, with some embracing these innovations with minimal restrictions, while others impose stringent regulations. This discrepancy may lead to substantial inequalities in AI integration across continents, affecting job markets and economic development.
Moreover, cultural factors play a crucial role in how societies adapt to AI. Different attitudes toward technology can shape the speed and effectiveness of its adoption, impacting how individuals and organisations leverage AI in their daily operations. Despite the advancements, the human brain remains indispensable, with AI serving as a powerful ally that enhances our capabilities rather than replaces them.
As we reflect on these developments, one might wonder how this article will age and how the points discussed will evolve over the next decade. Will we see a more harmonious collaboration between humans and AI, or will disparities widen? The future is uncertain, but it is clear that adaptability and a proactive approach will be essential as we navigate this new landscape. How do you envision your role in shaping the future of work in this rapidly changing environment?
Key takeaways:
AI’s workforce impact – AI is reshaping industries, bringing both new opportunities and concerns about job displacement
Job security in flux – many roles will evolve rather than vanish, requiring workers to adapt to new skill demands
Skills for the future – data analysis and AI management are becoming essential as automation changes job requirements
AI as a partner – most AI applications enhance human work, boosting productivity rather than replacing workers
Industry-specific shifts – AI adoption varies by sector, transforming jobs differently in healthcare, manufacturing, and creative fields
Cultural & economic factors – AI’s impact depends on economic trends and societal attitudes, requiring strategic adaptation
The power of human skills – as automation increases, critical thinking and emotional intelligence will be more valuable than ever
Thriving in the AI era – businesses and employees must understand and adapt to AI’s evolving role to stay ahead
Coming Next:
In my upcoming article, I will dive into the less talked about side of the gig economy, exploring how older workers are navigating the unpredictable world of freelance and contract work. From financial instability to mental health pressures, this article sheds light on the real struggles faced by an often-overlooked demographic.
Curious to learn more? Stay tuned for a deep dive into the untold realities of gig work!
Sources used to write this text: