The gig economy and older workers: opportunity or unfair struggle?
Why flexible work is not always the solution for an ageing workforce
Gig work is often praised for its flexibility, but does it truly work for everyone? For younger professionals, it may offer freedom and independence, but for older workers, it often means financial instability, lack of benefits, and an uncertain future. As traditional job security erodes, many are left wondering—does the gig economy create opportunities, or does it push older workers into an unfair struggle?
What You Will Learn in This Article:
The key challenges older workers face in the gig economy, from job insecurity to physical strain
How the lack of benefits and protections makes gig work unsustainable for many in later life
The financial risks older gig workers encounter, including irregular income and the absence of retirement plans
How isolation and the lack of professional support affect older gig workers' well-being.
The implications of the evolving gig economy for older generations' future employment prospects
The Gig Economy and Older Generations: A Growing Challenge
The gig economy presents vastly different experiences depending on the nature of the work. Office-based professionals may appreciate the flexibility of remote, freelance opportunities, but for those in physically demanding jobs, the challenges are far greater. Older workers in these roles often struggle with job security, benefits, and physical well-being.
While younger workers may view gig work as an opportunity for autonomy and career exploration, older generations face unique obstacles that make participation far less appealing. The instability, lack of benefits, and absence of social protections pose serious risks, particularly for those approaching or in retirement.
The Struggle for Stability
One of the most pressing issues for older gig workers is job insecurity. Traditional employment offers long-term stability, predictable income, and career progression. Gig work, by contrast, is highly unpredictable, with no guarantees of consistent work or income. Many older workers, whether by choice or necessity, find it difficult to achieve financial stability.
According to the Gig Economy Index, 55% of gig workers cite irregular income as a major challenge, making financial planning difficult. Older workers often face additional financial pressures, such as mortgages, medical expenses, and retirement planning. A report by the UK Trades Union Congress (TUC) found that older gig workers are 40% more likely to experience financial hardship compared to their traditionally employed peers.
The Absence of Benefits and Protections
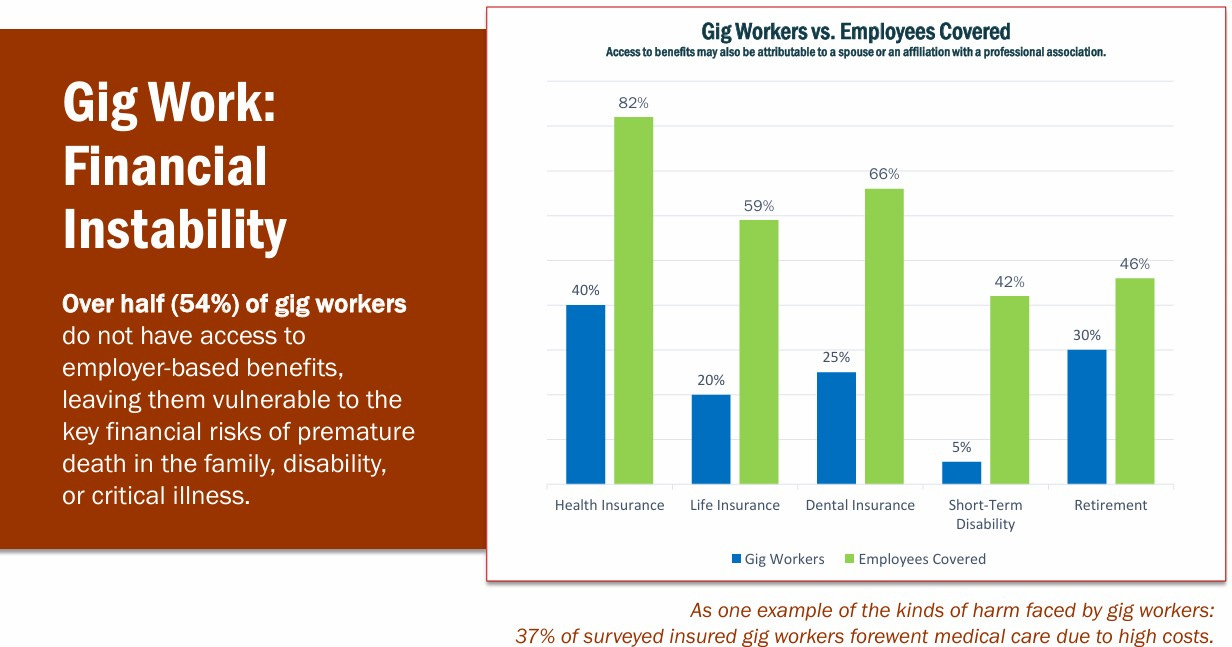
A major disadvantage for older gig workers is the lack of benefits. Traditional employment typically includes health insurance, paid leave, and retirement contributions—essential safety nets for those with increasing medical needs. Gig workers, classified as independent contractors, must secure these on their own. For many, this added financial burden makes gig work unsustainable in the long term. Over half (54%) of gig workers do not have access to employer-based benefits, leaving them vulnerable to the key financial risks of premature death in the family, disability, or critical illness. In the UK, a 2022 Resolution Foundation report found that nearly two-thirds of self-employed workers lack a pension plan, increasing the risk of financial insecurity later in life. Moreover, gig workers do not qualify for minimum wage guarantees, overtime pay, or unemployment benefits. The International Labour Organization (ILO) has highlighted that older gig workers are particularly vulnerable to precarious working conditions, often lacking a financial safety net in times of crisis.
Isolation and Lack of Professional Support
However, the impact of these financial struggles extends beyond just numbers and statistics—it often leads to emotional and mental strain. As older gig workers grapple with the absence of benefits and the stress of managing their own health insurance and retirement plans, they also face the growing challenge of isolation. Traditional workplaces offer not just a salary but also a social network and professional support. Gig workers, on the other hand, work in relative solitude, which can be particularly difficult for older workers accustomed to more structured environments. This lack of social interaction and professional development opportunities can amplify the feelings of uncertainty and stress caused by financial instability. Research from the University of Manchester found that older gig workers report higher stress levels and greater anxiety compared to younger counterparts, highlighting the dual burden of financial insecurity and emotional isolation.
The Race to the Bottom
Competition in the gig economy can drive down wages, particularly for older workers in high-cost-of-living countries. Platforms such as Upwork and Fiverr allow global competition, where younger workers or those in lower-wage regions can undercut prices.
A 2023 European Commission study found that gig economy wages have declined by an average of 20% over the past five years, with older workers experiencing even steeper drops in earnings. For those relying on gig work as their primary income source, this downward pressure on wages makes financial stability increasingly difficult to achieve.
A Precarious Future
The expansion of the gig economy raises concerns about the future of work, particularly for older generations. As companies turn to gig workers to cut costs, traditional full-time employment opportunities may become scarcer. This shift reduces job quality and make retirement planning even more uncertain for workers in their 50s and 60s.
Addressing these challenges requires action from policymakers and businesses. Solutions such as portable benefits, stronger legal protections, and better access to retirement savings options could help mitigate some of the difficulties faced by older gig workers. The World Economic Forum has recommended universal portable benefits systems, allowing gig workers to retain benefits even as they switch between jobs and platforms. Without such measures, the gig economy may continue to disadvantage older generations, leaving them in a precarious financial and professional position.
Final Thoughts: A Precarious Future for Older Workers?
The gig economy offers flexibility and new opportunities, but for older workers, it also brings significant risks. Without job security, benefits, or professional support, many struggle to make gig work sustainable. Research highlights a troubling reality—older gig workers face greater financial instability, weaker social protections, and increased mental health challenges compared to those in traditional employment.
As the workforce evolves, will older workers be supported, or will they be left to navigate an increasingly precarious job market alone? Should policymakers and businesses step up to create fairer protections, or is this just the new reality of work? If gig work continues to grow, what does it mean for the future of retirement?
Key Takeaways:
Older workers in the gig economy face greater financial insecurity due to unpredictable income and limited job stability
The absence of benefits such as healthcare, pensions, and paid leave makes gig work unsustainable for many older workers
Isolation and the lack of workplace support contribute to higher stress and mental health challenges
Older gig workers often struggle with digital platforms and limited access to skills development
Wage competition in the gig economy drives down earnings, making it harder for older workers to secure fair pay
The growing reliance on gig work threatens the availability of stable, full-time employment for older generations
Coming next:
The dust may have settled, but is the Great Resignation truly behind us? Signs of another shift are emerging—one that could reshape the labour market once again. Is the Big Stay a lasting transformation, or just a temporary pause before the next wave of change? The answers may surprise you. Stay with us as we uncover what is on the horizon.
Sources used to write this article:
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gig Economy (Businesses and Employees)
What are the pros and cons of working in the gig economy? | Barclay Simpson
The Rise of the Gig Economy: Benefits, Drawbacks, and Future Prospects
Can't Retire, Can't Find Jobs: Older Americans' Work, Money Struggles - Business Insider
Gig Work on the Rise Among Older Adults as Demand for Workplace Flexibility Grows
Digitalization’s Impact on Older Workers’ Entrepreneurship - Evidence-to-Impact Collaborative
Older Americans Taking Blue-Collar Jobs, White-Collar Hiring Slowdown - Business Insider
The health of workers in the global gig economy | Globalization and Health